앞선 포스트에서, api gateway 에 대해서 개괄적으로 알아보았다.
이번 포스트는 spring cloud gateway 를 통해 api gateway 를 구현하는 방법에 대해서 알아볼 것이다.
https://pius712.tistory.com/12
api gateway 란?
1. 외부 api 설계 이슈 마이크로 서비스의 경우, 모노리식과는 다르게 서비스에 직접 접근하여 api 를 호출하는 것은 여러가지 문제가 될 수 있다. 모놀리식인 경우에는 하나의 서비스에 api 를 호
pius712.tistory.com
참고로, 기존 api gateway 는 WebFlux 기반인데, 최근 mvc 기반으로도 api gateway를 구성할 수 있게 되었다.
1. 라우팅
자세한 내용에 대해서는 이후에 좀 더 보도록하고, 라우팅 동작에 대해서 살펴보자.
1.1 선언적 방식
선언적 방식으로 라우팅을 구현하는 방식.
api gateway 서버를 8080 포트로 띄우고, 다른 서버하나를 8081 서버로 띄운다.
@Component
class ServiceApiFilter : AbstractGatewayFilterFactory<ServiceApiFilter.Config>(Config::class.java) {
class Config
override fun apply(config: Config?): GatewayFilter {
return GatewayFilter { exchange, chain ->
log.info("service api filter: $uri")
val mono = chain.filter(exchange)
mono
}
}
}
application.yaml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: order-service-api
uri: <http://localhost:8081>
predicates:
- Path=/order-service/public-api/**
filters:
- name: ServiceApiFilter
위 코드를 작성한 후, 8081 번 포트의 서버에 /order-service/public-api/hello 컨트롤러 생성한다.
그리고, api gateway에 아래 요청을 하면, 8081 서버로 요청이 들어간다.
curl -X GET "<http://localhost:8080/order-service/public-api/hello>"
-H "Content-Type: application/json"
1.2 프로그래밍 방식
선언적 방식이 아닌 프로그래밍 방식으로도 라우팅이 가능하다.
위 코드를 프로그래밍방식으로 변경한다면 아래와 같다. (application yml 의 내용은 지우도록 하자)
@Configuration
class RouteConfig(
private val serviceApiFilter: ServiceApiFilter
) {
@Bean
fun gatewayRoutes(builder: RouteLocatorBuilder): RouteLocator {
return builder.routes()
.route { spec ->
spec.order(-1) // 우선순위
spec.path("/order-service/public-api/**") // 매칭할 주소
.filters { f ->
// 필터 지정
f.filter(serviceApiFilter.apply(PrivateFilter.Config()))
}.uri("http://localhost:8081") // 라우팅할 주소
}.build()
}
}2. 필터
spring security 와 같은 라이브러리와 마찬가지로, spring api gateway도 필터가 많이 활용된다.
여러 필터들을 선언 해두면, 해당 필터들을 거쳐서 실제 서비스로 라우팅이 된다.
그렇다면 필터에서는 어떤 일들을 할 수 있을까?
- WebFilterFactory 를 통해서, http request 와 http response 를 수정할 수 있다.
- 요청 전과 후에 어떤 동작을 수행할 수 있다. 예를들어, 인증 또는 로깅과 같은 작업을 할 수 있다.
2.1 전역 필터
global filter 의 경우, 모든 요청에 대해 동작하는 필터이다.
GlobalFilter 를 구현하고, bean 으로 등록만 해주면, 동작 하게 된다.
global filter 는 여러 개를 등록할 수 있고, Ordered 인터페이스를 구현하여서, 순서를 조정할 수 있다.
필터가 호출되는 방식은 일반적인 다른 필터와 마찬가지다.
참고로, global filter 이든 GatewayFilterFactory 로 생성된 필터든 순서를 지정하지 않으면 마음대로 동작한다.
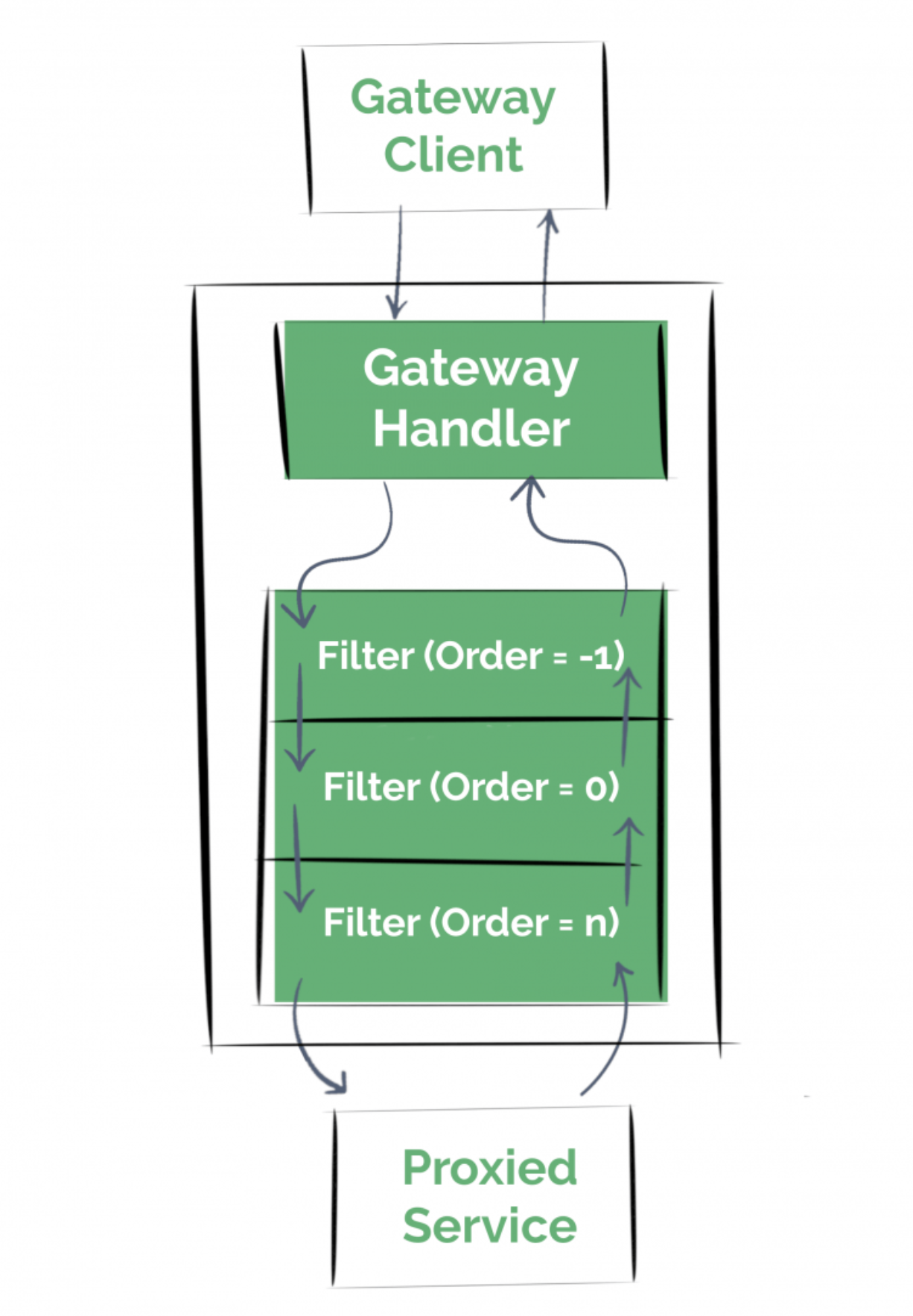
2.2 GatewayFilter - 설정 방식
일부 경로에 대해서만 적용되는 필터를 작성하고 싶을 수 있다. 이것이 GatewayFilter 이다.
AbstractGatewayFilterFactory 추상 클래스를 제공해주는데, 이를 구현하면 쉽게 구성할 수 있다.
gateway filter 작성
@Component
class ServiceApiFilter : AbstractGatewayFilterFactory<ServiceApiFilter.Config>(Config::class.java) {
private val log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(javaClass)
class Config(
val preLog: Boolean = false,
val postLog: Boolean = false
)
override fun apply(config: Config?): GatewayFilter {
return GatewayFilter { exchange, chain ->
val uri = exchange.request.uri
log.info("service api filter: $uri")
if (config?.preLog == true) log.info("service api filter: pre log")
val mono = chain.filter(exchange)
if (config?.postLog == true) log.info("service api filter: post log")
mono
}
}
}
설정파일로 gateway filter 등록하기
// application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: order-service-api
uri: <http://localhost:8081>
predicates:
- Path=/order-service/public-api/**
filters:
- name: ServiceApiFilter
config 설정하기
내부 클래스의 Config 에 설정 값을 넣을 수 있다.
@Component
class ServiceApiFilter : AbstractGatewayFilterFactory<ServiceApiFilter.Config>(Config::class.java) {
private val log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(javaClass)
class Config(
val preLog: Boolean = false,
val postLog: Boolean = false
)
override fun apply(config: Config?): GatewayFilter {
return GatewayFilter { exchange, chain ->
val uri = exchange.request.uri
log.info("service api filter: $uri")
// 설정 기반 로깅
if (config?.preLog == true) log.info("service api filter: pre log")
val mono = chain.filter(exchange)
// 설정 기반 로깅
if (config?.postLog == true) log.info("service api filter: post log")
mono
}
}
}
// application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: order-service-api
uri: <http://localhost:8081>
predicates:
- Path=/order-service/public-api/**
filters:
- name: ServiceApiFilter
args:
preLog: true
postLog: true
2.2 GatewayFilter - programmatic
application yaml 과 같은 설정파일이 아니라, 동적(프로그래밍 방식)으로 gateway filter 를 작성할 수도 있다.
@Configuration
class RouteConfig(
private val someFilter: someFilter
) {
@Bean
fun gatewayRoutes(builder: RouteLocatorBuilder): RouteLocator {
return builder.routes()
.route { spec ->
spec.order(-1) // 우선순위
spec.path("/some-api/**") // 매칭할 주소
// 필터 지정
.filters { f ->
f.filter(privateFilter.apply(PrivateFilter.Config()))
}.uri("http://localhost:8081") // 라우팅할 주소
}.build()
}
}이런 경우에는, 운영용 어드민을 통해 설정을 storage로 부터 읽는다거나 혹은 cloud config 와 같은 외부 설정 파일을 읽어서 설정들을 적용하는 방식도 가능하게 된다.
'스프링클라우드' 카테고리의 다른 글
| resilience4j - 서킷브레이커 (0) | 2024.10.05 |
|---|
